n today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, spatial computing has emerged as a groundbreaking concept that has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with digital content and the physical world around us. Combining elements of augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), computer vision, and sensor technologies, spatial computing offers immersive and interactive experiences that blur the boundaries between the digital and physical realms. This article explores the fundamentals, applications, and future implications of spatial computing.
Understanding Spatial Computing
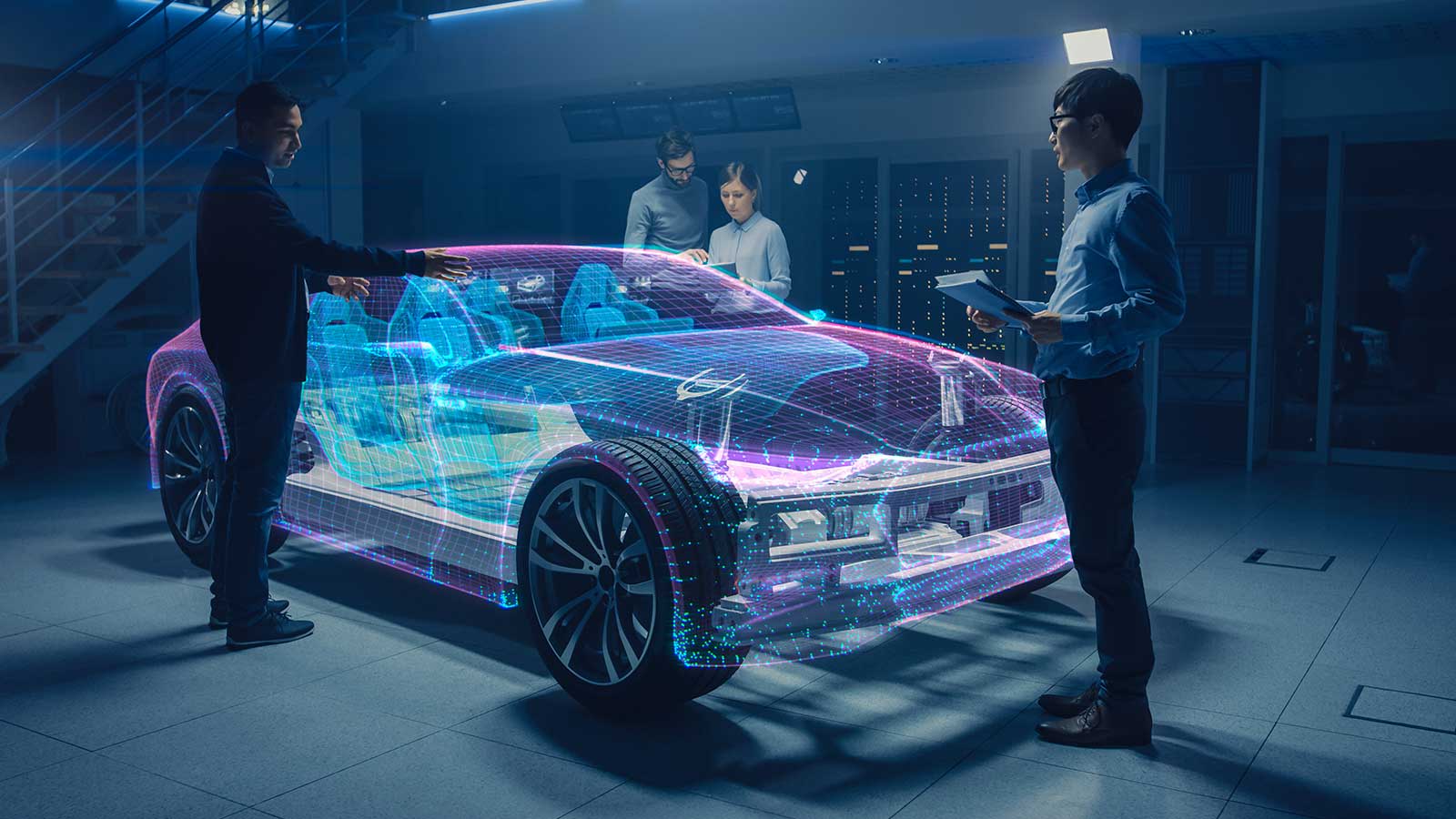
At its core, spatial computing involves the understanding and interpretation of space and spatial relationships by computers. It enables the real-time mapping of digital objects onto the physical environment, creating a seamless fusion of the virtual and real worlds. By leveraging sophisticated algorithms, advanced sensors, and computer vision techniques, spatial computing allows users to interact with digital content in a natural and intuitive manner.
Applications of Spatial Computing
Gaming and Entertainment: Spatial computing has revolutionized the gaming and entertainment industry, providing immersive and realistic experiences. AR and VR technologies allow gamers to step into virtual worlds, interact with virtual objects, and engage in captivating gameplay.
Education and Training: Spatial computing has enormous potential in education and training. It enables the creation of immersive simulations and virtual environments, providing learners with hands-on experiences that enhance understanding and retention. From medical training to architectural design, spatial computing opens new avenues for experiential learning.
Architecture and Design: Spatial computing has transformed the field of architecture and design. Architects can visualize and manipulate virtual building models in real-world environments, facilitating better planning, design validation, and client communication.
Healthcare and Medicine: Spatial computing offers promising applications in healthcare and medicine. Surgeons can use AR overlays to enhance surgical precision, medical students can explore virtual anatomy, and patients can benefit from personalized AR visualizations of their conditions.
Retail and E-commerce: Spatial computing has the potential to revolutionize the retail industry. AR allows customers to virtually try on clothes, visualize furniture in their homes, and experience products in a lifelike manner, enhancing the shopping experience.
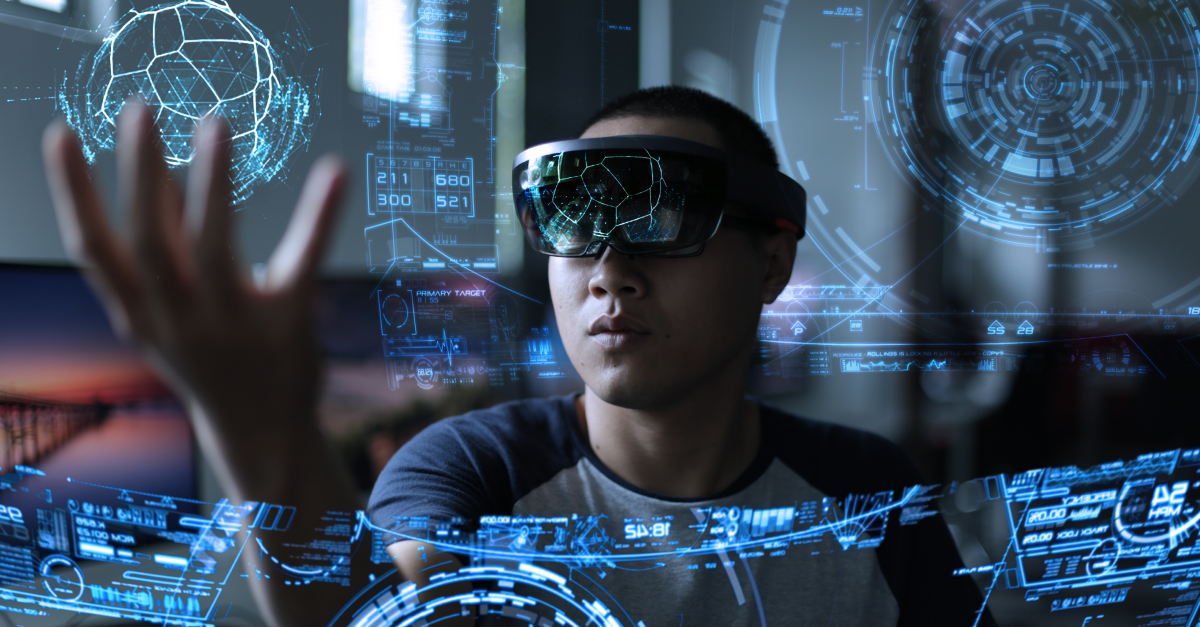 |
| source: Google |
Challenges and Future Implications
While spatial computing holds immense potential, several challenges must be addressed. These include the need for improved tracking accuracy, reduction of device size and cost, and the development of more intuitive user interfaces. Additionally, privacy and ethical considerations must be carefully addressed as spatial computing becomes more prevalent in our daily lives.
Looking ahead, the future of spatial computing is promising. Advancements in hardware, software, and algorithms will lead to more immersive and realistic experiences. As the technology becomes more accessible, we can expect to see its widespread adoption across various industries, transforming the way we work, learn, and play.
 |
| source: Google |
Spatial Computing is a groundbreaking technology that offers a multitude of benefits and opportunities. Here are some reasons why Spatial Computing is gaining significant attention:
Enhanced User Experience: Spatial Computing creates immersive and interactive experiences that engage multiple senses, providing users with a more intuitive and natural way to interact with digital content. It allows for seamless integration of virtual objects into the real world, offering a heightened level of immersion and engagement.
Real-world Integration: Spatial Computing enables the overlay of digital information onto the physical environment, effectively merging the virtual and real worlds. This integration has transformative implications across various industries, including gaming, education, healthcare, architecture, and more. It allows for the visualization of data and digital content in real-world contexts, improving understanding and decision-making.
Improved Human-Computer Interaction: Spatial Computing technologies, such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), provide novel ways to interact with computers and digital content. They eliminate traditional input barriers, such as keyboards and mice, and instead allow users to engage through natural gestures, voice commands, and physical movements. This creates more intuitive and immersive interactions, enhancing usability and accessibility.
Visualization and Simulation: Spatial Computing enables the visualization of complex data and models in three-dimensional space. Architects can visualize buildings, doctors can explore medical scans, and engineers can examine prototypes, all within realistic and interactive virtual environments. This capability aids in better understanding, analysis, and decision-making.
Experiential Learning: Spatial Computing has tremendous potential in education and training. It provides immersive and interactive simulations that allow learners to gain hands-on experience and explore concepts in a practical manner. Whether it's virtual field trips, medical simulations, or interactive science experiments, Spatial Computing enhances the learning process by making it more engaging, memorable, and effective.
Innovation and Industry Disruption: Spatial Computing is driving innovation and disrupting traditional industries. It opens up new possibilities for creating novel products, services, and experiences. Businesses are leveraging Spatial Computing to differentiate themselves, improve customer engagement, and drive growth. It's a catalyst for digital transformation and a competitive advantage in today's technology-driven world.
Future Potential: Spatial Computing is still in its early stages, with immense potential for further advancement and application. As technology evolves, we can expect improved hardware capabilities, more sophisticated algorithms, and increased accessibility. This will lead to even more immersive experiences, expanded use cases, and widespread adoption across various domains.
Conclusion
Spatial computing represents a paradigm shift in human-computer interaction, offering unprecedented opportunities to bridge the physical and digital worlds. By seamlessly integrating virtual content into our real-world environments, spatial computing enhances our ability to visualize, interact, and understand information. As this transformative technology continues to evolve, its impact will extend across industries, shaping the way we live, work, and connect with the world around us.
peoples also search for
"Spatial Computing: Exploring the Future of Immersive Technology""Unlocking the Potential of Spatial Computing: Revolutionizing Human-Computer Interaction"
"The Rise of Spatial Computing: Reshaping Industries and Experiences"
"Demystifying Spatial Computing: A Guide to Understanding the Virtual-Physical Convergence"
"Spatial Computing: Redefining the Boundaries of Reality"
"Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, and Beyond: The Power of Spatial Computing"
"Spatial Computing in Healthcare: Transforming Diagnosis, Treatment, and Patient Care"
"Spatial Computing for Education: Enhancing Learning through Immersive Experiences"
"Spatial Computing and Architecture: Designing the Future of Building and Planning"
"Spatial Computing in Gaming: Unlocking New Dimensions of Interactive entertainment
Post a Comment